Read Now
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready... |
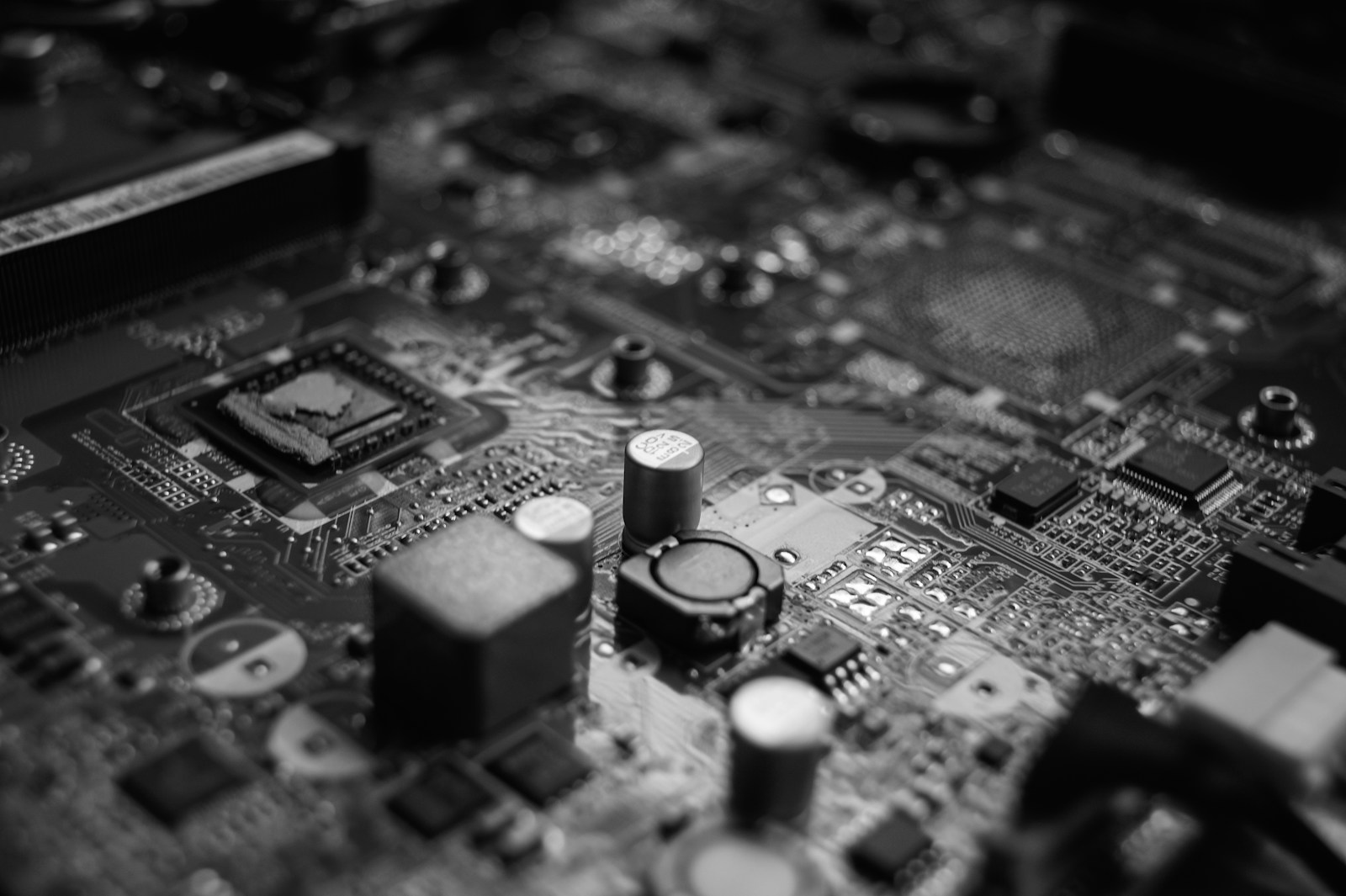
Micro ATX Motherboard
Understanding Micro ATX Motherboard Parts: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to building a custom PC, one of the most crucial components is the motherboard. It’s the central hub connecting all the other parts of a computer, and its form factor determines how your entire system is built. Among the different motherboard sizes available—such as ATX, Mini ITX, and E-ATX—the Micro ATX (mATX) strikes an ideal balance between performance, size, and affordability.
In this guide, we’ll delve into the intricate world of Micro ATX motherboard parts. Whether you’re a PC-building enthusiast or a beginner looking to learn more, this article will walk you through everything you need to know about the parts of a micro ATX motherboard, how they work, and why they matter.
What is a Micro ATX Motherboard?
Micro ATX (mATX) motherboards are a popular mid-size form factor standardized by Intel in 1997. Measuring 9.6 x 9.6 inches (244 x 244 mm), the mATX offers a compact alternative to standard ATX boards while retaining most of their functionality.
Key advantages of micro ATX motherboards include:
- Smaller footprint for more compact builds
- Compatibility with ATX and mATX cases
- Lower cost than full-sized ATX boards
- Adequate expandability with 2 to 4 RAM slots and multiple PCIe lanes
Now, let’s break down the major components and connectors you’ll find on a typical Micro ATX motherboard.
1. CPU Socket
The CPU socket is the physical interface between the motherboard and the central processing unit (CPU). This socket determines the type of CPU the motherboard can support. Intel and AMD use different socket types—such as LGA 1200, LGA 1700 for Intel, and AM4 or AM5 for AMD.
Key points:
- Located near the center-top of the board
- Surrounded by VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules) and power phases
- Protected by a metal or plastic retention bracket
- You must match your CPU type to the correct socket
Tip: Never force a CPU into a socket—it should fit snugly without pressure.
2. RAM (Memory) Slots
RAM slots, also called DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) slots, are where the system memory is installed. Most mATX boards come with two to four RAM slots, supporting dual-channel memory configurations.
Important features:
- Color-coded pairs for dual-channel optimization
- Support for various speeds (DDR4, DDR5)
- Maximum RAM capacity varies by board (typically 64GB to 128GB)
Check your motherboard’s QVL (Qualified Vendor List) for compatible RAM brands and speeds.
3. Chipset
The chipset acts as the motherboard’s control center, managing data flow between the CPU, memory, storage, and peripherals. It dictates many features, such as:
- Number of PCIe lanes
- USB ports and versions (e.g., USB 3.2 Gen 2)
- SATA ports
- Overclocking capabilities
- Compatibility with Intel Optane Memory (on some Intel boards)
The chipset is usually covered by a heatsink and is located near the bottom-left quadrant of the board.
Popular chipsets include:
- Intel: B760, H610, B660
- AMD: B550, A520, B650
4. Power Connectors
Micro ATX motherboards require several power connectors to function:
- 24-pin ATX power connector: Main power line from the PSU to the motherboard.
- 8-pin (or 4+4 pin) CPU power connector: Powers the CPU directly.
- Fan headers (3-pin or 4-pin): Connect case and CPU fans for cooling.
These connectors are typically located along the edges of the board to reduce cable clutter.

5. VRMs and Power Phases
Voltage Regulator Modules (VRMs) manage the voltage delivered to the CPU and other critical components. A quality VRM setup is essential for stable performance, especially if you plan to overclock.
VRMs are typically placed next to the CPU socket and covered by aluminum heatsinks to dissipate heat.
Key considerations:
- More VRM phases = better power distribution and cooling
- Heatsink coverage = improved thermal efficiency
- High-end boards have digital VRMs for more precise control
6. PCIe Expansion Slots
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots are used to install expansion cards such as GPUs, sound cards, and network adapters.
On a Micro ATX board, you’ll usually find:
- 1 x PCIe x16 slot: For graphics cards
- 1 or 2 x PCIe x1 or x4 slots: For add-in cards
Some modern boards may also offer PCIe 4.0 or PCIe 5.0 slots, which provide faster data transfer rates, especially beneficial for gaming and content creation.
Note: The physical length of the slot does not always match the number of lanes it supports.
7. Storage Connectors
Modern mATX boards support multiple types of storage interfaces:
SATA Ports
- Typically 4 to 6 on mATX boards
- Used for connecting HDDs and SATA SSDs
- Provide speeds up to 6Gbps
M.2 Slots
- Used for NVMe SSDs, offering faster read/write speeds than SATA
- Can be mounted horizontally with a screw
- Vary in size: 2230, 2242, 2280 (the number refers to width and length in mm)
High-end boards may have two or more M.2 slots, supporting RAID configurations or PCIe Gen 4 speeds.
8. Rear I/O Panel
The rear I/O panel houses all external connectivity options. It’s accessible from the back of the PC case and includes:
- USB ports: USB 2.0, USB 3.2 Gen 1, USB 3.2 Gen 2, and USB-C
- Ethernet port: For wired internet connectivity
- Audio jacks: Typically support 5.1 or 7.1 surround sound
- Video outputs: HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI (if the CPU has integrated graphics)
- PS/2 port: For legacy keyboards or mice
The exact configuration varies by manufacturer and model. High-end boards might include Wi-Fi antennas, BIOS flashback buttons, or optical audio out (S/PDIF).
9. Front Panel Headers
Located at the bottom of the motherboard, these headers connect to the case’s front I/O ports, such as:
- Power switch
- Reset switch
- Power LED
- HDD activity LED
- Front USB ports
- Front audio jack
Aligning these connectors correctly is crucial during installation. Manufacturers usually print labels or include a diagram in the manual for easy reference.
10. BIOS/UEFI Chip
The BIOS (Basic Input Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) chip contains the motherboard’s firmware. It handles hardware initialization and provides a user interface to configure system settings.
Key features of modern UEFI firmware:
- Graphical interface with mouse support
- Advanced settings for overclocking and fan control
- Boot priority settings
- Secure Boot and TPM options for Windows 11
Some motherboards also offer dual BIOS chips for redundancy and safer firmware updates.
11. Onboard Audio
Most micro ATX motherboards come with integrated audio chipsets, typically Realtek or ALC series, providing:
- High-definition audio (up to 24-bit / 192kHz)
- Multi-channel surround support (5.1 or 7.1)
- Audio capacitors for noise reduction
- Optical or analog outputs
While onboard audio is sufficient for most users, audiophiles may still prefer dedicated sound cards.
12. Networking Components
Networking on mATX boards is usually handled by:
- Gigabit Ethernet controller (Realtek, Intel, or Killer)
- Wi-Fi module (available on select models with Wi-Fi 5 or Wi-Fi 6 support)
- Bluetooth module (often paired with Wi-Fi cards)
Some premium micro ATX motherboards include 2.5 GbE Ethernet or Wi-Fi 6E, offering faster connectivity for gaming and streaming.
13. Diagnostic Tools
Premium micro ATX boards may also feature:
- Debug LEDs: Indicate boot issues by lighting up specific components (CPU, RAM, VGA, Boot)
- Post code displays: Show hexadecimal codes for diagnosing problems
- BIOS Flashback button: Lets you update firmware without a CPU or RAM installed
- Clear CMOS button or jumper: Resets the BIOS to default settings
These tools are particularly useful for enthusiasts and overclockers.
Conclusion: Is a Micro ATX Motherboard Right for You?
Micro ATX motherboards offer an excellent blend of features, expandability, and affordability in a compact form factor. They’re ideal for users who want performance without the bulk of a full-size tower or the limitations of a Mini ITX board.
To summarize, a Micro ATX motherboard typically includes:
- CPU socket
- RAM slots (2–4)
- Chipset and VRMs
- PCIe expansion slots
- SATA and M.2 storage interfaces
- Power connectors
- Rear I/O panel
- BIOS/UEFI firmware
- Front panel headers
- Onboard audio and networking
When choosing a micro ATX board, consider your CPU compatibility, storage needs, GPU clearance, and expansion options. Brands like ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, and ASRock offer a wide range of mATX boards to suit every use case, from budget builds to high-performance rigs.
By understanding the individual parts of a micro ATX motherboard, you can make more informed decisions when assembling or upgrading your PC, ensuring every component works in harmony for the best possible computing experience.
FAQs
1. What is a Micro ATX motherboard?
A Micro ATX (mATX) motherboard is a mid-sized motherboard form factor measuring 9.6 x 9.6 inches (244 x 244 mm). It balances performance, expandability, and compact size.
2. How is Micro ATX different from ATX and Mini ITX?
- ATX: Larger, more expansion slots, better airflow.
- Micro ATX: Mid-sized, fewer slots than ATX, more than Mini ITX.
- Mini ITX: Smallest, limited expansion, ideal for compact builds.
3. What CPU sockets are used on Micro ATX motherboards?
Micro ATX motherboards use the same sockets as ATX boards, including LGA 1200, LGA 1700 for Intel, and AM4, AM5 for AMD.
4. How many RAM slots does a Micro ATX motherboard have?
Typically, 2 to 4 RAM slots, supporting dual-channel memory configurations.
5. Can Micro ATX motherboards support gaming GPUs?
Yes, most Micro ATX boards have at least one PCIe x16 slot, which supports full-sized graphics cards.
6. What chipsets are available for Micro ATX motherboards?
Popular chipsets include Intel B760, H610, AMD B550, A520, and B650, depending on the processor.
7. Can I overclock with a Micro ATX motherboard?
Yes, if the board has a chipset and VRM design that supports overclocking (e.g., Intel Z-series or AMD B/X-series).
8. How many M.2 slots are usually on a Micro ATX motherboard?
Most mATX boards have 1 to 2 M.2 slots for NVMe SSDs.
9. Do Micro ATX boards support Wi-Fi and Bluetooth?
Some models include built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, while others require add-in cards or USB adapters.
10. How many PCIe slots does a Micro ATX motherboard have?
Typically 3 to 4 total PCIe slots, including 1 PCIe x16 and 2–3 x1/x4 slots.
11. What power connectors are required for a Micro ATX motherboard?
- 24-pin ATX main power
- 4 or 8-pin CPU power connector
Additional fan or RGB headers may also be present.
12. Are Micro ATX boards compatible with ATX cases?
Yes, most ATX cases support Micro ATX motherboards. Just check the case’s specifications.
13. Can I use Micro ATX in a Mini ITX case?
No, Micro ATX boards are larger and will not fit in Mini ITX cases.
14. How much RAM can a Micro ATX motherboard support?
Usually between 32GB and 128GB, depending on the board and chipset.
15. What storage options are available on Micro ATX boards?
- SATA ports for SSDs and HDDs
- M.2 slots for NVMe SSDs
- Some support RAID configurations
16. Is onboard audio good on Micro ATX motherboards?
Yes, most come with high-definition Realtek or ALC audio chips, suitable for general use and gaming.
17. What kind of rear I/O ports do Micro ATX boards have?
Common ports include:
- USB (2.0, 3.2, USB-C)
- HDMI/DP/DVI
- Ethernet
- Audio jacks
- Sometimes Wi-Fi antennas
18. Are Micro ATX motherboards cheaper than ATX?
Yes, mATX boards are generally more affordable while still offering similar features for most users.
19. Do all Micro ATX motherboards support RGB lighting?
Not all. Some include RGB/ARGB headers for lighting control, while others do not.
20. What is the maximum GPU size I can use on a Micro ATX board?
Most GPUs fit, but case size and clearance matter more than the board size itself. Always check the case specifications.
21. Do Micro ATX boards support dual GPUs?
Not commonly. Most mATX boards have only one PCIe x16 slot, making multi-GPU setups impractical.
22. Are Micro ATX motherboards good for gaming?
Yes, especially for mid-range to high-end builds. They support modern CPUs, GPUs, fast storage, and memory.
23. Do Micro ATX boards support USB-C?
Some newer boards include USB-C ports on the rear I/O or headers for front-panel USB-C.
24. Can I build a silent or low-power PC with Micro ATX?
Yes. You can pair a Micro ATX board with low-TDP CPUs, passive coolers, and silent fans to build a quiet system.
25. What brands make the best Micro ATX motherboards?
Top motherboard brands include:
- ASUS (TUF, Prime)
- MSI (MAG, Pro)
- Gigabyte (B-series, AORUS)
- ASRock (Steel Legend, Pro series)